Facebook OAuth is used to
communicate between Applications & Facebook users, to grant
additional permissions to your favorite apps. To make this possible,
users have to 'allow or accept' the application request so that app can
access your account information with required permissions.
As a normal Facebook user we always think that it is better than
entering your Facebook credentials, we can just allow specific
permissions to an app in order to make it work with your account.
Today whitehat Hacker 'Nir Goldshlager' reported 'The Hacker News' that
he discovered a very critical vulnerability in Facebook's OAuth system,
that allowed him to get full control over any Facebook account easily
even without 'allow or accept' options.
For this purpose he hunt the flaw in a very mannered way i.e
Step 1) Understanding the OAuth URL
Step 2) Finding a way to use custom parameters in URL
Step 3) Bypassing OAuth 'Allow' button request at user end
1.) Understanding the OAuth URL
The Facebook OAuth dialog URL is something like shown below:
https://www.facebook.com/dialog/oauth/?app_id=YOUR_APP_ID&next=YOUR_REDIRECT_URL&state=YOUR_STATE_VALUE&scope=COMMA_SEPARATED_LIST_OF_PERMISSION_NAMES
Where
app_id is the application ID and
next parameter must contains the URL of the respective app domain only. For example
app_id=2389801228 belongs to '
Texas Holdem Poker' app, So the '
next' parameter will allow only
zynga.com domain (i.e
next=http://zynga.com), otherwise Facebook will block that action.
2.) Finding a way to use custom parameters in URL
Goldshlager found that Facebook was allowing him to use facebook's sub domain in next parameter in the URL ie. https://beta.facebook.com/#xxx!/messages/. But '#xxx!' was not working for all browsers. After fuzzing the URL characters, he found that %23~! and %23%09! worked for all browsers.
This finding was enough to redirect user to any file or folder at Facebook domain.
Then he developed a simple Facebook application
(i.e touch.facebook.com/apps/testestestte) ,which was just to redirecting users to remote site (
i.e. files.nirgoldshlager.com) with access token, where a log file was ready to store all access tokens.
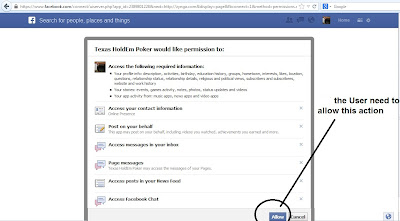
3.) Bypassing OAuth 'Allow' button request at user end
Till now attacker was able to redirect user to a fake app, which was
passing victim's access tokens to a 3rd party domain where attacker was
logging access tokens. But the main issue was still there i.e without
user interaction, app will not work. That means, one have to click 'allow' button as shown below.
So, to bypass this, he discovered that there are many built-in Facebook applications i.e 'Facebook Messenger app'
that can access full permissions (read inbox, outbox, manage pages,
manage ads,access to private photos, videos, etc.) from the victim's
account without user interaction i.e no need to click 'allow' button.
i.e Sample Final URL :
https://www.facebook.com/connect/uiserver.php?app_id=220764691281998&next=https%3A%2F%2Ftouch.facebook.com%2F%23~!%2Fapps%2Ftestestestte%2F&display=page&fbconnect=1&method=permissions.request&response_type=token
This way attacker is now able to grab
access tokens (with full permissions) of any Facebook account by just
making his victims to visit a modified OAuth URL (without user interaction). This access_token will be never expired, It will expired only after the victim change his Facebook password
As a responsible bug hunter,
Nir Goldshlager
reported this flaw to Facebook security team few months back and now it
is fixed. He was rewarded many times in bug bounty program. In January
he also reported a
password reset vulnerability in Facebook Employees Secure Files Transfer service
Note: This tutorial is only
for Educational Purposes, I did not take any responsibility of any
misuse, you will be solely responsible for any misuse that you do.
Hacking email accounts is criminal activity and is punishable under
cyber crime and you may get upto 40 years of imprisonment, if got caught
in doing so.